Managing tenant insurance is a crucial element in overseeing commercial real estate (CRE) from a landlord and commercial property management perspective. All landlords and commercial property managers should require tenants to have various forms of insurance depending on the type of business operations occupying the relevant space. Tenant insurance comes in several forms. Business renters’ insurance helps pay to repair or replace business property if it is damaged or stolen. Commercial general liability (CGL) insurance helps protect against third-party injuries and property damage. Finally, business owner’s insurance is a combination of business renter’s insurance and a CGL policy. All these policies serve as a protective measure shielding tenants from potential financial losses arising from damage to their personal belongings or liability for on-site accidents. Typically, landlords mandate tenants to maintain various forms of insurance coverage as a prerequisite or addendum to commercial lease agreements.
For those involved in the commercial real estate (CRE) scene, grasping the basics of tenant insurance is crucial. Landlords and property managers need to familiarize themselves with the ins and outs of insurance policies and coverage details to verify tenants’ compliance with lease agreement terms. It falls on the shoulders of landlords and property managers to guarantee tenants possess sufficient insurance coverage. Employing insurance tracking solutions can be a helpful step, allowing them to track insurance certificates and ensure they stay current, which we look at more in depth below.
Understanding Basic Tenant Insurance in Commercial Real Estate
Business Renter’s Insurance
Business renter’s insurance serves as a comprehensive risk management solution for commercial lessees, which is typically mandated by leases. This specialized insurance coverage goes beyond the standard commercial property protection, offering nuanced financial safeguards which help both the tenant and the landlord. It typically includes coverage for business interruption, liability arising from customer interactions, and protection for valuable equipment or inventory that is installed or stored at the leased premises.
For sophisticated stakeholders in the business world, this insurance provides a conservative approach to mitigating risks associated with leased commercial spaces. This type of insurance is designed to address the unique challenges and potential financial exposures that businesses may encounter due to common losses associated with commercial operations, aligning with the complex nature of their unique operations.
These insurance policy terms are often customizable to meet the specific needs of different industries and businesses, allowing for a tailored risk management strategy. The coverage may encompass scenarios such as property damage, legal liabilities, and even cyber threats that could impact business operations. In essence, business renter’s insurance for a modern commercial audience represents a strategic investment in safeguarding assets, ensuring business continuity, and protecting against a range of potential financial setbacks.
Commercial General Liability Insurance
Commercial General Liability (CGL) insurance for commercial tenants is a comprehensive risk management tool and/or policy designed to help protect commercial business tenants from a wide range of potential liabilities. These policies can be tailored for those with a nuanced understanding of commercial business operations, this insurance typically goes beyond basic coverage to address the complex challenges and legal intricacies that sophisticated commercial enterprises may face on a day-to-day basis.

Key features of CGL insurance for a sophisticated commercial tenant audience include:
- Broad Form Coverage: CGL insurance provides protection and coverage for third-party bodily injury, actual property damage, and personal and advertising injury claims that are related to the insured’s operations. This type of policy acts as a financial shield against lawsuits and legal expenses arising from alleged negligence or unintentional harm caused by the business. Depending on the type of policy that the commercial tenant has, claims made or occurrence policies, there are limits as to the insurance underwriter’s exposure. Moreover, even if the policy was “blown up” and no more coverage existed the insurance company still has a duty to defend the commercial tenant in any lawsuit.
- Legal Defense Costs: Typically, CGL policies include coverage for legal defense costs, encompassing attorney fees, court expenses, and settlements or judgments. This is crucial for businesses navigating complex legal disputes, however as stated above some policies have burning limits as to the full amount of the policy.
- Risk Management Expertise: Insurers offering CGL coverage to a sophisticated commercial tenant audience may provide additional risk management services. This could include direct or video consultations, comprehensive safety training for key personnel, and other current initiative-taking measures to help commercial businesses mitigate potential risks and reduce the likelihood of liability claims.
- Customization Options: CGL policies can be narrowly or broadly tailored to meet the specific needs of different commercial industries and businesses. This ensures that the CGL coverage aligns with the unique risks associated with commercial business operations.
- Excess Liability Protection: For commercial businesses with substantial assets and exposures, excess liability coverage may be necessary. This extends the coverage limits beyond the standard policy limits, providing an extra layer of financial protection. Obviously, the more insurance coverage the more the premiums will cost.
- International Coverage: Given the global nature of many commercial businesses, CGL policies may offer coverage in the form of riders or addendums for liability arising from international operations. This is of paramount importance for companies with a global footprint.
Commercial general liability insurance for a commercial tenant is a necessity as it serves as a strategic and potentially comprehensive risk management tool, offering financial protection and support tailored to the specific challenges faced by commercial businesses in today’s complex and interconnected commercial business landscape.

Business Owner’s Insurance
Business Owner’s Insurance is a combination of business renter’s insurance and commercial general liability insurance which can be narrowly or broadly tailored for a sophisticated commercial operation. This insurance package, often referred to as a Business Owner’s Policy (BOP), goes beyond standard coverage, providing a sophisticated and nuanced approach to protecting commercial businesses against a multitude of risks.
Key aspects of BOP Insurance include:
- Property Insurance: Covers physical assets such as buildings, business equipment, and inventory against a broad spectrum of perils, including fire, theft, and natural disasters. These policies include coverage for not only owned property but also leased or rented premises and contents.
- Liability Protection: Similar to a typical CGL policy this provides coverage for third-party bodily injury or property damage claims, as well as legal defense costs.
- Business Interruption Coverage: Importantly, BOP policies address the budgetary impact of disruptions to business operations caused by covered perils. This can include reimbursement for lost income and ongoing expenses during the recovery period, but it is crucial for business owners to have well documented operations to not be scrambling after an event has occurred.
- Cyber Liability Insurance: Given the increasing digitalization of business operations, sophisticated BOPs often include addendums or rider coverage for data breaches, cyberattacks, and related liabilities. This additional coverage protects against the financial fallout of cybersecurity incidents.
- Professional Liability (Errors and Omissions) Coverage: For businesses that provide professional services, BOPs may offer coverage for claims of negligence or failure to perform professional duties adequately. For example, brokers, property managers, attorneys all have a duty to carry E&O insurance for their operations.
- Employment Practices Liability Insurance (EPLI): EPLI policies protect against claims related to commercial employment practices, including any type of discrimination, wrongful termination, and various types of harassment. This is paramount for a commercial operation and is particularly relevant in today’s complex and litigious business environment.
- Directors and Officers (D&O) Insurance: Safeguards the personal assets of company executives and directors in the event they are personally sued for alleged wrongful acts in managing the business provided the act that is sought to be covered was in the normal course of business.
- Customization and Endorsements: BOPs underwriters often allow for customization and modification to their policies to meet specific business needs. Additional endorsements and riders can be added to address unique risks faced by a particular commercial business.
In summary, Business Owner’s Insurance for a commercial tenant audience is a comprehensive and tailored risk management solution that recognizes the multifaceted challenges businesses encounter. It provides a broad and important approach to protect against a wide range of liability and risks, offering financial security and strategic support for the complex landscape of modern commercial enterprises.
Why Pay for Commercial Insurance Tracking?
Commercial tenant insurance tracking for landlords and property managers is a meticulous and necessary process that ensures compliance with insurance requirements outlined in commercial lease agreements. Insurance tracking acknowledges the complex nature of commercial real estate (CRE) transactions, tenants, and sub-tenants, and aims to safeguard the interests of both landlords and tenants. Here are key aspects:
- Policy Verification: Required by competent commercial property managers is a vigorous verification of tenant insurance policies by conducting and scrutinizing insurance coverage details and confirming that those details align with the insurance requirements in the commercial lease agreements. This requires and involves a detailed understanding of insurance terminology and coverage requirements.
- Comprehensive Coverage Assessment: Top-level commercial tenant insurance tracking goes beyond just looking at the basic coverage requirements in lease agreements. Importantly it also involves assessing the adequacy and amounts of coverage for potential risks, including property damage, liability claims, and business interruption. The primary principal behind this is to hopefully ensure that commercial tenants have the robust protection a landlord would like to have as compared to the range of insurable contingencies.
- Real-Time Monitoring Solutions: Utilization of advanced insurance tracking solutions (via a dashboard) provides real-time data into the status of commercial insurance certificates. This enables immediate identification of any lapses or deficiencies, allowing landlords and commercial property managers to address issues promptly.
- Customized Compliance Management: Tailoring commercial tenant insurance tracking processes to the specific needs of different commercial properties and industries is a hallmark of sophistication and the advancement of technology. This process involves creating custom templates for insurance compliance checklists and protocols based on the unique risks associated with each property- and this data is available via a dashboard that landlords and commercial property managers have full-time access to.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies Employed: Beyond insurance tracking, commercial tenant insurance management involves the development and implementation of proactive risk mitigation strategies which requires a level of insurance coverage knowledge. This can include recommending broad risk reduction measures to commercial tenants and providing resources to enhance overall property safety.
- Staff Legal Compliance Expertise: Given the intricate legal landscape of commercial real estate, sophisticated tenant insurance tracking should include a deep understanding of relevant laws and regulations by the landlord or commercial property manager. This safeguard will help ensure that the insurance requirements align not only with the lease language, but also with legal standards and that any changes in insurance regulations or building owner requirements are promptly addressed.
- Constant Communication with Tenants: Clear and effective communication with tenants is integral and paramount to a successful commercial landlord tenant relationship. A competent commercial property manager in place of the landlord should have effective continuous communication with the commercial tenants. Sophisticated processes include transparent communication about insurance requirements, any updates, and any necessary actions or updates about the policies. This fosters a cooperative relationship between landlords and tenants and property management personnel.
- Integration with Property Management Systems: Integration with sophisticated property management systems allows for seamless coordination between tenant insurance tracking and overall commercial property management operations. A monitored property management dashboard enhances efficiency and accuracy in insurance compliance monitoring.
Ideally, commercial tenant insurance tracking for a sophisticated real estate audience is a comprehensive and initiative-taking process that combines diligence, industry expertise, and advanced technology. It ensures that landlords, tenants, and commercial property managers are well-positioned to navigate the complexities of commercial real estate while maintaining a secure and compliant environment.

Insurance Coverage Details
Top level commercial landlords and commercial property managers will monitor the insurance policies of their tenants, but it is important for commercial tenants to understand their own coverage details to ensure they are adequately protected in case of an event or a loss.
Understanding Coverage Limits and Deductibles
The specific coverage limits and deductibles of individual policies will vary based on factors such as the type of commercial business, industry, location, and the terms negotiated with the landlord. Here are some common types of commercial insurance coverage for commercial tenants and a summary of coverage limits and deductibles:
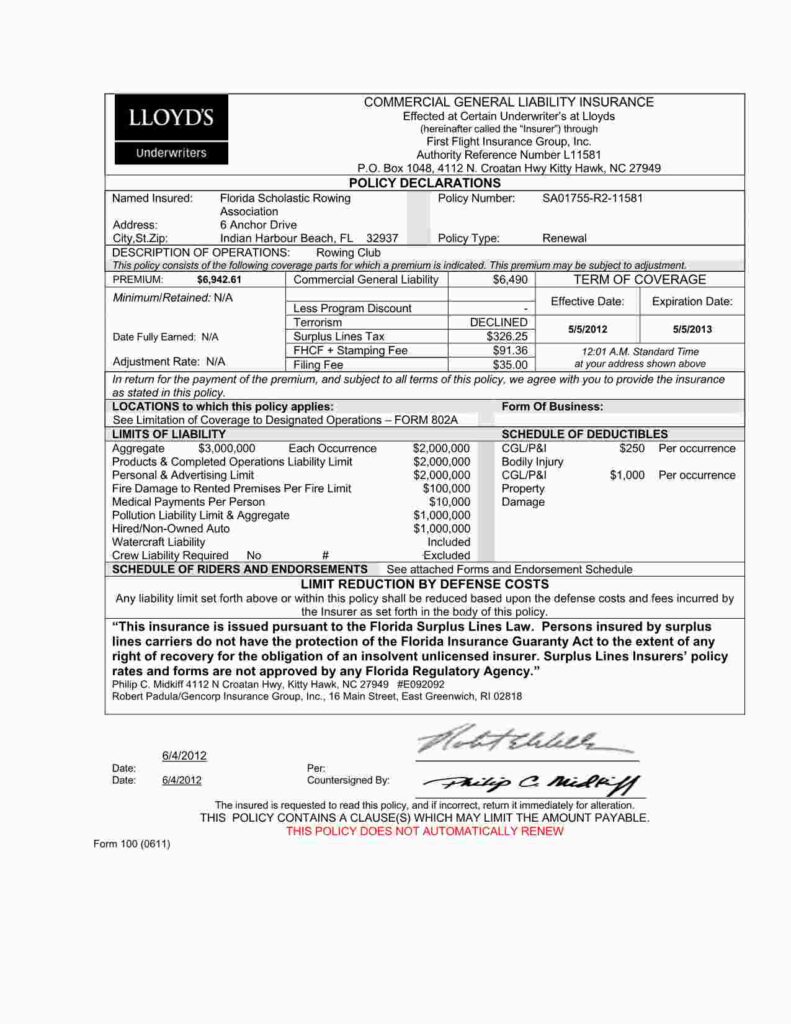
Commercial General Liability (CGL) Insurance:
Coverage Limits: Commercial general liability insurance typically covers third-party bodily injury, property damage, and personal injury claims. Coverage limits can vary, but common limits range from $1 million to $2 million per occurrence with an aggregate limit (total limit for the policy term). Some hazardous operations require up to $5 million in coverage.
Typical Deductible: The deductible is the amount the tenant must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Deductibles can vary, and a higher deductible often leads to lower premium costs.
Commercial Property Insurance:
Coverage Limits: Property insurance covers the tenant’s business property, including inventory, equipment, and fixtures. Coverage limits depend on the value of the insured property. It is crucial to ensure that the coverage amount is sufficient to replace or repair damaged or lost property. Common limits range from $1 million to $2 million per occurrence.
Deductible: Like CGL insurance, property insurance comes with a deductible. The tenant can choose a deductible amount that suits their risk tolerance and budget. It is not uncommon for a deductible amount in the $2,500 to $5,000 range.
Business Interruption Insurance:
Coverage Limits: Business interruption insurance provides coverage for lost income and additional expenses if the business is temporarily unable to operate due to a covered peril (e.g., fire, flood). Coverage limits are typically tied to the business’s expected revenue (burden of proof is on the tenant) and expenses during the interruption period.
Deductible: Business interruption insurance typically has a waiting period before coverage begins, and a deductible will also apply.
Coverage Limits: Umbrella insurance provides additional liability coverage beyond the limits of the primary liability policies (such as CGL). It acts as a secondary layer of protection and should be large enough to cover a catastrophic event.
Deductible: Umbrella policies may have a self-insured retention (SIR), which is a form of deductible that must be satisfied before the umbrella coverage applies.
Workers’ Compensation Insurance:
Coverage Limits: Workers’ compensation insurance provides coverage for actual employees’ medical expenses and lost wages due to work-related injuries or illnesses. Coverage limits are often mandated by state regulations.
Deductible: Not common.
Commercial tenants should carefully review and understand their insurance policies, including coverage limits and deductibles, to ensure they have adequate protection for their specific business needs. It is advisable to consult with insurance professionals or brokers who specialize in commercial insurance to tailor coverage to the unique risks of the business. Additionally, landlords and property managers will have specific insurance requirements outlined in the lease agreement that tenants must meet or exceed.

The Role of Landlords and Property Managers
When it comes to commercial tenant insurance tracking, landlords and commercial property managers play a key role in ensuring ongoing compliance with insurance requirements in leases.
Managing Certificates of Insurance
Once insurance requirements are established in the lease, landlords and property managers must manage the process of collecting and tracking certificates of insurance (COIs) from tenants.
COIs serve as proof of insurance coverage and should be received before tenants move in and on an ongoing basis as policies due dates are approached. Landlords and commercial property managers should also ensure that the COIs meet the minimum requirements specified in the lease and that they are valid and up to date.
To manage COIs effectively, landlords and commercial property managers should be utilizing a COI management system. These systems can automate the process of collecting, tracking, and verifying COIs, reducing the risk of errors, and ensuring compliance with insurance requirements.
Commercial Insurance Tracking Solutions
Commercial insurance tracking systems are software tools or services designed to help landlords and commercial property managers manage and monitor their tenant’s insurance policies. These systems are particularly valuable for landlords and commercial property managers with multiple insurance policies, varying coverage types, and compliance requirements. See overview below:
Policy Management
Centralized Database: Sophisticated commercial insurance tracking systems maintain a centralized database where landlords and commercial property managers can store and organize information about their tenant’s insurance policies. Obviously, all the pertinent data include details such as underwriters, claims addresses and notice requirements, policy numbers, coverage types, coverage limits, and renewal dates.
Renewal Tracking
Automated Renewal Notifications: One of the key features of these software systems is the ability to automate the tracking of insurance policy renewal dates. The system sends notifications to relevant stakeholders, tenants, and officers of the business, well in advance of renewal deadlines, helping commercial tenants avoid coverage gaps. The insurance brokers also have a notice system for their clients, but the landlord and commercial property manager will also notify the tenants.
Insurance Compliance Monitoring
Insurance Policy Compliance Checks: Insurance tracking systems often include features to ensure that the commercial tenant remains compliant with regulatory requirements and individual lease agreements. This involves checking that coverage limits meet specified thresholds or that specific types of insurance are in place – which is all handled within the software systems.
Insurance Document Management
Digital Document Storage: Sophisticated tracking systems often provide a secure platform for storing and managing insurance-related documents, such as policy documents, certificates of insurance, and endorsements. Having a centralized repository simplifies document retrieval and audit processes. Commercial property managers have storage capabilities and should have 24/7 backup software to prevent malware or hacking attacks.
Integration with Other Property Management Systems
Integration Capabilities: Many commercial insurance software tracking systems can integrate with other business systems, e.g., enterprise resource planning (ERP) software or risk management platforms. Integration streamlines data flow and ensures consistency across various organizational functions and provides efficiency in the commercial property management arena.
Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to Regulations: Commercial tenant insurance tracking systems assist businesses in adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards. This is especially important for commercial tenants operating in highly regulated sectors.
Landlords and commercial property managers implementing a commercial insurance tracking system can enhance efficiency, reduce the risk of underinsurance or non-compliance, and provide a comprehensive overview of the landlord’s risk management strategy. Commercial property managers can choose between in-house software solutions or opt for third-party monitoring services that specialize in insurance tracking and compliance management.
Which Insurance Tracking System?
In the process of selecting an insurance tracking system the specific needs of the landlord and the specific class of tenants is important to consider. Of the more popular insurance tracking systems Building Engines, SmartCompliance, and Datex Property Solutions are the leaders.
Commercial property managers should look for a system that is user-friendly and customizable to their specific needs. The system should also provide robust reporting capabilities to help property managers track compliance and identify areas for improvement. The level of tech support and customer service provided by the insurance tracking system is paramount to a successful integration with your current systems and prevents long downtimes.
Final Thoughts
In search of a trustworthy and professional commercial property management collaborator, Esquire Property Management Group exemplifies a steadfast commitment to adhering to legal and ethical protocols and we understand the importance of commercial tenant insurance confirmation and tracking.
David currently is the broker/owner of several real estate related businesses which manage and maintain 300+ client properties on the San Francisco Peninsula.
Trust, transparency, and performance guarantees are the foundation of these businesses. David challenges anyone to find a PM professional that offers services similar - extensive education, customer service, and performance guarantees.
David also provides consulting for his clients on property development feasibility, construction, and complex real estate transactions.
David has authored a published law review article, three real estate books, and over 150+ real estate blog articles.
- “Wildfires, Insurance & Mortgages: Will Your Home Survive the Financial Aftermath?” - March 3, 2025
- What’s Driving California’s Commercial Real Estate Shakeup? - February 27, 2025
- Critical Issues in Triple Net Leases Investors Should Know - February 14, 2025

